Manufacturing Software: Benefits, Features, and Key Types
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, manufacturing software plays a crucial role in optimizing production, improving efficiency, and ensuring seamless operations. Whether managing supply chains, automating workflows, or enhancing quality control, the right software can streamline manufacturing processes and drive business growth.
However, choosing the best fit for your business can be challenging with a wide range of manufacturing software solutions available – from ERP and MES systems to AI-driven analytics and cloud-based platforms.
This blog will explore the different types of manufacturing software, key features to look for, and how these solutions can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and future-proof your operations. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
- What is Manufacturing Software?
- What are the Benefits of Manufacturing Software?
- Key Types of Manufacturing Software
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
- Human Resources Management System (HRMS)
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) Software
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) Software
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) & Smart Factory Solutions
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software
- Quality Management Systems (QMS) Software
- Key Features to Look for in Manufacturing Software
- How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Software for Your Business
- Manufacturing Software Development with Kaopiz
- Future Trends in Manufacturing Software
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is Manufacturing Software?
Manufacturing software is a digital solution designed to help businesses manage and optimize their production processes, inventory, supply chain, and quality control. It enables manufacturers to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance decision-making by automating workflows and providing real-time data insights.
Nowadays, companies must streamline operations and embrace digital transformation to stay competitive. Manufacturing software plays a critical role in this transition, offering tools to manage everything from raw material procurement to final product delivery.
What are the Benefits of Manufacturing Software?
Manufacturing software provides end-to-end solutions to help businesses automate, optimize, and scale their production processes. Below are the key benefits of implementing manufacturing software:
Increased Efficiency & Automation
Manufacturing software automates monotonous tasks and optimizes production workflows, leading to:
- Faster production cycles with automated scheduling and resource allocation
- Reduced manual errors by digitizing data entry and quality control
- Optimized machine performance with predictive maintenance alerts

Cost Reduction & Waste Minimization
One of the biggest advantages of manufacturing software is its ability to cut costs and minimize waste through:
- Optimized raw material usage to prevent overproduction
- Energy-efficient operations by monitoring and adjusting machine performance
- Lower labor costs by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks
Therefore, businesses can reduce operational costs and maximize profitability.
Better Data-driven Decision-Making
With real-time analytics and AI-powered insights, manufacturers can make smarter, data-backed decisions in areas like:
- Demand forecasting to align production with market trends
- Inventory management to prevent stock shortages or overstocking
- Production performance tracking to identify bottlenecks and optimize workflows
By leveraging data, businesses can improve strategic planning, risk management, and operational efficiency.
Improved Supply Chain Visibility
A connected supply chain ecosystem helps manufacturers:
- Track raw materials, components, and finished goods in real time
- Monitor supplier performance to prevent delays
- Enhance logistics and distribution planning for faster delivery

Scalability & Flexibility for Growth
Manufacturing software supports businesses at every stage of growth by offering:
- Cloud-based solutions for seamless scalability
- Flexible integrations with ERP, CRM, and IoT systems
- Multi-location support for businesses with multiple production sites
As production demands increase, businesses can expand operations without overhauling existing systems, ensuring long-term sustainability and competitiveness.
Key Types of Manufacturing Software
There are many types of manufacturing systems available in the market. Some systems focus on production management, while others enhance supply chain visibility, customer relationships, or product design.
The right manufacturing software depends on a company’s size, industry, and production needs. To help manufacturers choose the best solution, we have listed 9 commonly used types of manufacturing software:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
- Human Resources Management System (HRMS)
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) Software
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) Software
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) & Smart Factory Solutions
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software
- Quality Management Systems (QMS) Software
Each software type plays a critical role in modern manufacturing by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and driving digital transformation. Let’s scroll down as we explore their key functionalities and benefits of each type.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software
ERP software is a powerful solution designed to streamline and integrate multiple business processes into a single, centralized system. For manufacturing companies, ERP software plays a crucial role in optimizing production, inventory, supply chain, procurement, financial management, and compliance, allowing businesses to operate with greater efficiency and real-time visibility.

Advantages of ERP Manufacturing Software
Disadvantages of ERP Software
Who should use ERP software?
ERP solutions are best suited for large and mid-sized manufacturers with complex operations and multiple business units.
Industries that benefit from ERP software include:
- Construction & Engineering: For project management and procurement tracking.
- Manufacturing & Industrial Production: To streamline supply chains and improve shop floor efficiency.
- Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals: To ensure regulatory compliance and manage resources efficiently.
- Retail & Consumer Goods: For inventory control and multi-channel sales management.
- Waste Management & Environmental Services: To track materials, costs, and regulatory compliance.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
A MES is a specialized software solution that helps manufacturers track, monitor, and control production processes in real time. By bridging the gap between ERP systems and the shop floor, MES software improves operational efficiency, quality control, and compliance while providing manufacturers with data-driven insights to optimize production.

- Real-time monitoring and automated workflows reduce errors and speed up processes.
- Tracks defects, ensures quality control, and supports regulatory compliance.
- Provides real-time data analytics for performance tracking and predictive maintenance.
- Minimizes material waste and enables just-in-time inventory management.
- Works with ERP, IoT, and AI-driven technologies for a connected factory.
- Requires significant investment in software, hardware, and maintenance.
- Needs skilled IT personnel to connect with ERP, IoT, and automation systems.
- Workers may need time and training to adapt to the new system.
- Stores sensitive production data, making it vulnerable to cyber threats.
- System failures or malfunctions can disrupt production.
MES solutions are ideal for manufacturers in industries that require real-time tracking, process optimization, and regulatory compliance, such as:
- Automotive & Aerospace: For tracking complex assembly processes and supply chains.
- Pharmaceutical & Medical Devices: To maintain strict quality control and regulatory compliance.
- Electronics & Semiconductor Manufacturing: For component tracking and defect detection.
- Food & Beverage: To manage batch tracking, ingredient traceability, and safety standards.
- Industrial Equipment & Heavy Machinery: To optimize machine performance and preventive maintenance.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
CRM software is a powerful tool that helps manufacturers manage customer interactions, track sales, and streamline communication. While CRM is often associated with sales and marketing, it plays a crucial role in manufacturing by improving customer relationships, optimizing sales pipelines, and ensuring better service delivery.

- Stores customer data, preferences, and history for personalized interactions.
- Tracks leads, sales, and orders to improve forecasting and efficiency.
- Automated service requests, warranty tracking, and customer communication.
- Analyzes customer behavior, sales trends, and market opportunities.
- Works with ERP, MES, and marketing automation tools for end-to-end business management.
- Advanced CRM solutions require investment in software, training, and customization.
- Employees need time and training to utilize CRM effectively.
- Storing sensitive customer information can pose cybersecurity threats if not well-protected.
- CRM software must be continuously updated to stay relevant and effective.
CRM software is ideal for manufacturers looking to enhance customer relationships and sales management, including:
- Industrial Equipment Manufacturers: To track orders, service requests, and customer history.
- Automotive & Aerospace: To manage B2B client relationships and supply chain demands.
- Food & Beverage: To handle distributor and retailer interactions efficiently.
- Electronics & Consumer Goods: To streamline customer service and after-sales support.
Human Resources Management System (HRMS)
HRMS is software that helps manufacturers manage employee data, payroll, recruitment, and workforce performance efficiently. In the manufacturing industry, where workforce coordination is crucial, HRMS plays a key role in ensuring compliance, tracking labor productivity, and automating HR processes.

- Stores and manages workforce records, attendance, and payroll in one system.
- Ensures accurate payroll processing and compliance with labor laws.
- Tracks employee performance, schedules shifts, and monitors labor efficiency.
- Streamlines hiring, onboarding, and training processes.
- Aligns workforce management with production planning and operational needs.
- Advanced HRMS solutions require investment in software, training, and customization.
- Requires integration with payroll, ERP, and time-tracking systems.
- Stores sensitive employee data, making it a target for cyber threats.
- Staff may need time and training to adapt to the system.
HRMS is essential for manufacturers managing large workforces, multiple shifts, and compliance-heavy environments, including:
- Automotive & Aerospace Manufacturing: To manage large teams and track workforce performance.
- Electronics & Heavy Machinery: To schedule shifts, monitor labor efficiency, and handle payroll.
- Food & Beverage Production: To ensure compliance with health and safety labor regulations.
- Textile & Apparel Manufacturing: To manage seasonal workers and track skill-based roles.
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) Software
PLM software helps manufacturers manage the entire lifecycle of a product, from initial design and development to production, distribution, and end-of-life management. By centralizing product data, PLM software ensures collaboration between engineering, manufacturing, and supply chain teams, improving efficiency and innovation.

Advantages of PLM Software
- Stores and organizes all product-related information in one system.
- Enables seamless communication between engineering, design, and manufacturing teams.
- Speeds up the design-to-production process with efficient workflow management.
- Ensures adherence to industry regulations and quality standards.
- Reduces errors, waste, and rework by improving product design and manufacturing processes.
Disadvantages of PLM Software
- Requires significant investment in software, implementation, and training.
- Needs to be integrated with ERP, MES, and CAD tools for full functionality.
- Employees need training to effectively use PLM features.
- Sensitive product design and intellectual property data may be vulnerable to cyber threats.
Who Should Use PLM Software?
PLM software is ideal for manufacturers focused on product design, innovation, and regulatory compliance, including:
- Aerospace & Automotive: To manage complex product designs and compliance with safety standards.
- Electronics & High-Tech Manufacturing: To track rapid product development cycles.
- Food & Beverage Industry: To ensure compliance with food safety regulations and packaging design.
- Apparel & Consumer Goods: To manage seasonal product designs and supply chain coordination.
Supply Chain Management (SCM) Software
SCM software helps manufacturers streamline procurement, production planning, inventory management, logistics, and supplier coordination. By providing real-time visibility into the supply chain, SCM software enables businesses to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.

Advantages of SCM Software
- Provides real-time tracking of raw materials, inventory, and shipments.
- Prevents overstocking and stockouts with demand forecasting.
- Streamlines procurement and vendor relationship management.
- Enhances operational efficiency, cutting unnecessary expenses.
- Ensures on-time delivery with automated logistics and distribution planning.
Disadvantages of SCM Software
- Advanced SCM solutions require significant investment.
- Needs to be integrated with ERP, MES, and logistics platforms for full functionality.
- Sensitive supplier and logistics data may be vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Inaccurate data entry can lead to inefficiencies and errors in supply chain planning.
Who Should Use SCM Software?
- Automotive & Aerospace: To track global suppliers, logistics, and component sourcing.
- Electronics & Machinery: To manage supply chain risks and ensure timely component availability.
- Food & Beverage: To monitor perishable goods and maintain regulatory compliance.
- Retail & Consumer Goods: To optimize warehouse management and ensure just-in-time inventory.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) & Smart Factory Solutions
IIoT and Smart Factory solutions leverage sensor technology, real-time data analytics, and automation to enhance manufacturing processes. These solutions enable manufacturers to connect machines, optimize production, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall efficiency.
- Tracks machine performance and production status in real-time.
- Uses AI and sensors to detect equipment issues before failures occur.
- Enhances production efficiency with automated workflows.
- Reduces waste and lowers operational costs.
- Improves coordination between production, inventory, and logistics.
- Requires significant infrastructure upgrades and IoT-enabled machinery.
- Connected devices are vulnerable to cyber threats and data breaches.
- Needs to be seamlessly integrated with legacy systems and enterprise software.
- Employees need training to operate and maintain IIoT systems.
IIoT and Smart Factory solutions are ideal for manufacturers aiming to digitize and optimize operations, including:
- Automotive & Aerospace: To enable predictive maintenance and automated production.
- Electronics & Machinery: To monitor equipment health and enhance production efficiency.
- Food & Beverage: To improve quality control and regulatory compliance.
- Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals: To ensure precision manufacturing and reduce downtime.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software
CAD software is essential for manufacturers involved in product development, prototyping, and engineering design. It enables designers and engineers to create, modify, analyze, and optimize detailed 2D and 3D models before production, reducing errors and improving efficiency.

- Creates accurate and detailed 2D/3D models.
- Enables teams to work together on designs in real time.
- Speeds up product development and reduces design errors.
- Minimizes material waste by refining designs before production.
- Works with CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) and PLM for a seamless workflow.
- Advanced CAD tools require significant investment.
- Designers and engineers need training to use complex CAD features.
- Requires powerful computing resources for 3D modeling.
- Large design files need proper storage and version control.
CAD software is essential for manufacturers focused on precision engineering and product innovation, including:
- Automotive & Aerospace: To design complex components and ensure high safety standards.
- Electronics & Machinery: To develop circuit boards, machinery parts, and mechanical systems.
- Textile & Apparel: To design patterns and optimize fabric use.
- Architecture & Construction: To create detailed building and structural designs.
Quality Management Systems (QMS) Software
QMS software helps manufacturers monitor, control, and improve product quality throughout the production process. It ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations, reducing defects and enhancing customer satisfaction.

- Ensures consistent quality control across production lines.
- Helps meet industry standards like ISO 9001, FDA, and GMP.
- Reduces paperwork and streamlines audits.
- Identifies and resolves quality issues early in production.
- Ensures raw materials meet required standards.
- Requires investment in software, training, and integration.
- Needs configuration to align with company-specific quality standards.
- Requires accurate data entry for effective quality control.
- Employees may need time to adapt to automated quality processes.
QMS software is essential for manufacturers in highly regulated industries and those prioritizing product quality, including:
- Automotive & Aerospace: To ensure safety, durability, and compliance with international standards.
- Electronics & Medical Devices: To track component quality and regulatory compliance.
- Food & Beverage: To manage hygiene, safety, and food quality standards.
- Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals: To maintain strict quality control in drug production.
Key Features to Look for in Manufacturing Software
Selecting the best manufacturing software systems for your requirements can be challenging. With numerous system development methods and vendors available, manufacturers often struggle to find the best fit for their needs.
Here, you will get clear about essential features compiled from our point of view to simplify the decision-making process.
AI & Data Analytics for Decision-Making
AI and data analytics are transforming the manufacturing industry by enabling smarter, data-driven decision-making. These technologies help manufacturers optimize production, predict equipment failures, and enhance overall efficiency.

Predictive analytics also minimizes downtime by identifying early signs of equipment failure, enabling proactive maintenance. Additionally, AI enhances supply chain forecasting, helping manufacturers manage inventory, anticipate demand, and streamline operations.
Production Planning & Scheduling
Look for manufacturing software that has production planning and scheduling features, so you can optimize resources, reduce bottlenecks, and improve efficiency. Automated tools adjust schedules in real time, ensuring smooth workflows and on-time deliveries.
By integrating real-time data, manufacturers can forecast production needs, manage labor and machine utilization, and coordinate operations more effectively. This leads to on-time deliveries, reduced waste, and improved cost management, making production planning software essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
Inventory & Supply Chain Management
Efficient inventory and supply chain management ensure manufacturers have the right materials at the right time, reducing delays and waste. Advanced software helps track stock levels, automate reordering, and optimize storage, preventing overstocking or shortages.
Real-time visibility across the supply chain improves supplier coordination, demand forecasting, and logistics planning. By streamlining inventory and supply chain processes, manufacturers can reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and improve overall production flow.
Quality Management & Compliance Tracking
Quality management feature helps manufacturers monitor product quality, detect defects, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Automated tracking systems enable real-time inspections, reducing errors and improving consistency.

With built-in compliance features, manufacturers can meet industry standards, maintain audit records, and streamline certification processes. This leads to higher product reliability, fewer recalls, and improved customer trust.
Scalability & Cloud Deployment
Scalable, cloud-based manufacturing software allows businesses to grow without limitations while ensuring seamless operations. Cloud deployment provides remote access, real-time data synchronization, and lower IT costs, making it a flexible solution for manufacturers of all sizes. With cloud-based sales management systems, manufacturers can easily scale production, integrate new technologies, and expand to multiple locations without expensive infrastructure upgrades. This ensures greater agility, improved collaboration, and enhanced security across the entire manufacturing process.How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Software for Your Business
Selecting the right manufacturing software is essential for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and staying competitive. Alongside multiple available options, all you must know is to define your specific needs to select the best solution that aligns with them.
Here are key factors to consider when making your decision:
- Functionality: Identify your biggest operational challenges and choose software that strengthens workflows, improves efficiency, and addresses key pain points.
- Reputable Provider: Research the software provider’s reputation, customer reviews, and industry experience to ensure reliability and long-term support.
- Subscription Model: Consider SaaS options that offer flexible monthly payments, reducing upfront costs and eliminating the need for expensive installations.
- Updates & Support: Ensure regular updates and customer support are included to maintain compliance, security, and access to the latest features.
- Scalability: Choose a solution that grows with your business, handling increased production volume and complexity without disruption.
- Budget & IT Compatibility: Assess your current IT setup and budget to find software that integrates seamlessly with existing systems and offers a strong return on investment.
Manufacturing Software Development with Kaopiz
At Kaopiz, we specialize in developing custom manufacturing software solutions tailored to your business needs. With expertise in IT outsourcing, cloud solutions, AI, and automation, we help manufacturers streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and drive digital transformation.
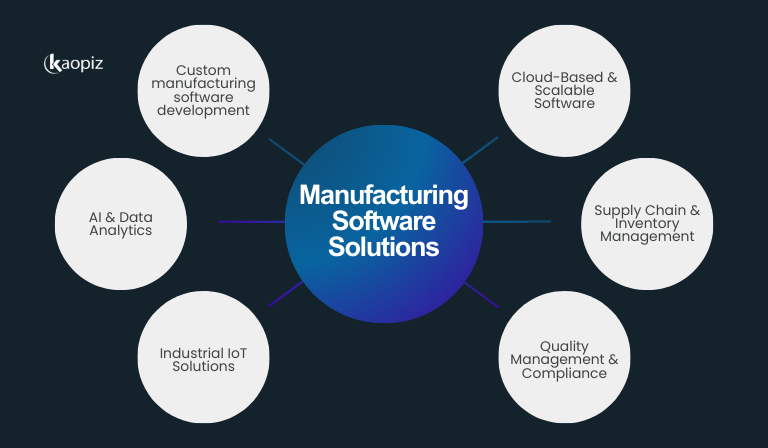
- Custom Manufacturing Software Development: Tailor-made solutions for production management, automation, quality control, and process optimization.
- AI & Data Analytics: Smart insights for demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, and operational optimization.
- Industrial IoT Solutions: Smart factory technologies for real-time equipment tracking, automated alerts, and remote monitoring.
- Cloud-Based & Scalable Software: Flexible, secure, and easily scalable solutions that adapt to your growing manufacturing needs.
- Supply Chain & Inventory Management: Digital tools to enhance logistics coordination, inventory accuracy, and cost optimization.
- Quality Management & Compliance: Ensure consistent product quality, regulatory compliance, and continuous improvement.
Moreover, with 500+ experts across various fields, 10+ years of experience, and a 98% customer satisfaction rate, Kaopiz is a trusted software development partner for businesses of all sizes. We combine industry expertise with cutting-edge technology to create manufacturing software that improves productivity, reduces costs, and supports business growth.
Explore success stories to see how we can develop a customized software solution to fit specific manufacturing challenges.
Future Trends in Manufacturing Software
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a major transformation, driven by technological advancements and the need for greater adaptability. As businesses navigate evolving global challenges, software innovation is reshaping traditional processes, leading to enhanced efficiency, sustainability, and resilience.
Here are the key manufacturing trends shaping the world in 2025 and beyond:
- Industry 4.0 and Smart Factories
- AI and Machine Learning Integration
- Sustainability and Circular Economy Practices
- Cybersecurity in Manufacturing
- Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE)
- Decentralized Manufacturing for Agility & Resilience
Conclusion
Manufacturing software is at the heart of modern industrial transformation, enabling businesses to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and adapt to evolving market demands. From ERP and MES systems to AI-driven analytics and cloud-based solutions, the right software can significantly improve production planning, supply chain management, and overall business agility.
As technology advances, trends like Industry 4.0, smart factories, AI integration, and sustainability will continue to shape the future of manufacturing. Choosing the right software requires careful consideration of functionality, scalability, security, and business needs to ensure long-term success.
Ready to transform your manufacturing operations? Contact Kaopiz today to explore how our solutions can help your business stay ahead in the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What’s the Best Manufacturing Software for a Small Business?
The best manufacturing software for a small business depends on specific needs, budget, and industry. Cloud-based ERP, or inventory management software with scalable features is often a good choice. Popular options include NetSuite, Odoo, and Katana. Custom software may also be ideal for businesses with unique requirements.
What’s the Difference Between ERP and MRP?
ERP is a comprehensive system that manages multiple business processes, including finance, HR, inventory, and production. MRP focuses specifically on manufacturing and inventory management, helping businesses plan material procurement and production schedules. While MRP is often a module within ERP, standalone MRP systems cater to manufacturers with simpler needs.
Is Custom Manufacturing Software Better Than Off-the-Shelf Solutions?
It depends on your business requirements. Off-the-shelf solutions are cost-effective and quick to implement but may lack flexibility. Custom software, like solutions developed by Kaopiz, is tailored to fit specific workflows, integrate seamlessly with existing systems, and scale with business growth. If your business has unique operational needs, custom software can provide greater efficiency and competitive advantage.
2 Replies to “Manufacturing Software: Benefits, Features, and Key Types”
Leave a Comment
Trending Post



















Pingback:Digital Transformation in Manufacturing: Benefits & Examples 2025
Pingback:Top 10 Manufacturing IT Trends to Watch in 2025