TypeScript vs JavaScript: Which One Should Singapore Leaders Choose in 2025?
In Singapore’s fast-paced digital economy, choosing the right technology stack is more than a technical decision — it’s a strategic investment. For years, JavaScript has powered nearly every website and web app worldwide. But today, its modern evolution, TypeScript, is reshaping how enterprises build scalable and reliable systems.
Backed by Microsoft, TypeScript brings strong typing, better error handling, and improved team collaboration, making it ideal for large, complex projects. As Singapore pushes forward with its Smart Nation and enterprise digitalization goals, many leaders are asking: Which delivers better long-term ROI — TypeScript or JavaScript?
This article compares TypeScript vs JavaScript in terms of performance, productivity, and business impact, and explores why more Singapore companies are choosing TypeScript in 2025.
Table of Contents
- What Is JavaScript?
- What Is TypeScript?
- How JavaScript and TypeScript Work
- What Are the Key Differences Between TypeScript vs JavaScript?
- Pros and Cons of TypeScript and JavaScript
- Performance, Productivity & ROI
- When to Use TypeScript vs JavaScript
- Offshore Advantages: Web Development Projects in Singapore
- Kaopiz: Your Trusted Partner for TypeScript vs JavaScript Development in Singapore
- Future Outlook in Singapore (2025–2030): TypeScript as the New Enterprise Standard
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What Is JavaScript?
JavaScript is one of the world’s most widely used programming languages, powering over 98% of websites and countless business applications. Originally developed in the mid-1990s, it remains the core technology of modern web development — alongside HTML and CSS.

For businesses, JavaScript’s main appeal lies in its versatility. It can run on both the client and server sides, enabling companies to build everything from interactive websites and e-commerce platforms to enterprise dashboards and SaaS products. Its vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks (like React, Vue, and Node.js) allows faster development cycles and easier integration with existing systems.
Because of its simplicity and massive talent pool, JavaScript remains the default choice for startups and SMEs looking to launch digital products quickly. However, as projects grow larger and more complex, some of JavaScript’s weaknesses — such as runtime errors and maintainability challenges — have become increasingly apparent, paving the way for TypeScript’s rise.
What Is TypeScript?
TypeScript is a programming language developed by Microsoft as an enhanced version of JavaScript. It adds a powerful feature called static typing, which allows developers to detect and fix errors before running the code — making projects more stable and easier to maintain.
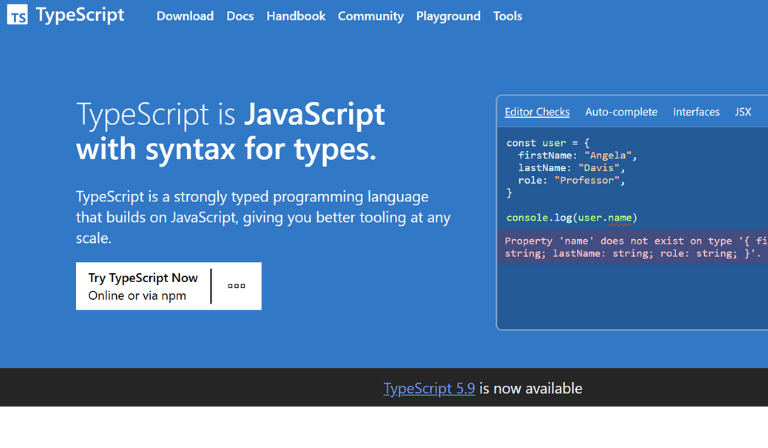
In simpler terms, TypeScript helps development teams write cleaner, safer, and more predictable code. It compiles into regular JavaScript, so any system or browser that supports JavaScript can run TypeScript-based applications.
For businesses, especially those managing large-scale or long-term projects, TypeScript offers clear advantages:
- Fewer bugs and lower maintenance costs
- Easier collaboration across distributed or offshore teams
- Better scalability as systems grow
Because of these benefits, global enterprises — including Airbnb, Slack, and Grab — have adopted TypeScript to improve productivity and reliability. In Singapore, more IT firms and digital solution providers are following this trend to support enterprise-grade development with greater consistency and ROI.
How JavaScript and TypeScript Work
JavaScript and TypeScript are closely connected — in fact, TypeScript is built on top of JavaScript. Every TypeScript program eventually compiles into standard JavaScript, which browsers and servers can execute. This means businesses adopting TypeScript don’t have to rebuild their systems from scratch; they can gradually integrate it into existing JavaScript codebases.
The key difference between JavaScript vs. TypeScript lies in when errors are detected.
- JavaScript checks for issues while the program is running, which can lead to unexpected bugs in production.
- TypeScript, on the other hand, catches errors during development through static typing — preventing costly runtime failures later.
From a business perspective, this early error detection translates into fewer production issues, smoother deployment, and reduced QA costs. For Singapore enterprises managing large teams or offshore collaborations, TypeScript’s structured workflow ensures greater code consistency and long-term stability, without sacrificing JavaScript’s flexibility and speed.
What Are the Key Differences Between TypeScript vs JavaScript?
While TypeScript and JavaScript share the same foundation, they differ in how they handle code structure, scalability, and error management. The table below highlights the most important distinctions between TypeScript vs JavaScript benchmarks that business leaders and technical teams should understand before choosing between the two.
| Criteria | JavaScript | TypeScript |
|---|---|---|
| Type System | Dynamic — data types are determined at runtime, which can lead to hidden errors. | Static — developers define data types in advance, preventing bugs early in development. |
| Compilation | Interpreted directly by browsers or Node.js. | Compiled into JavaScript before execution, ensuring code quality and consistency. |
| Error Handling | Errors appear only when the code runs, increasing the risk of production issues. | Errors are detected during development, reducing time spent on debugging. |
| Tooling | Basic support; relies heavily on external libraries. | Strong IDE integration with autocompletion, refactoring tools, and error hints. |
| Syntax & Features | Flexible but less structured, easier for small teams. | Structured, supports modern object-oriented features (interfaces, generics). |
| Learning Curve | Easier to start, faster for prototypes. | Slightly steeper, but improves long-term productivity and maintainability. |
TypeScript’s structure and type safety make it better suited for large-scale enterprise projects, while JavaScript remains a quick and flexible option for smaller or fast-moving development cycles.
Type System
The type system is one of the most significant differences between JavaScript and TypeScript comparison and it directly impacts software reliability and development efficiency.
- JavaScript uses a dynamic type system, meaning data types (like numbers, strings, or objects) are assigned at runtime. While this makes development faster in the early stages, it also increases the risk of undetected errors that can appear during operation, sometimes after deployment.
- TypeScript, in contrast, applies a static type system, where data types are explicitly defined during development. This allows developers to catch mistakes before the software runs, reducing bugs and saving debugging time.
For businesses, this means fewer production issues, lower maintenance costs, and greater predictability — especially when multiple developers or offshore teams are working on the same project.
Compilation
Compilation determines how code is processed and executed — and it’s another major difference between TypeScript vs JavaScript code comparison.
- JavaScript is an interpreted language, meaning the browser or server reads and executes the code directly. This makes it fast for simple applications, but can allow errors to surface only at runtime.
- TypeScript, on the other hand, must first be compiled (or “transpiled”) into JavaScript before running. During this process, the compiler checks the code for errors and inconsistencies, ensuring that only clean, reliable JavaScript is deployed.
From a business standpoint, this compilation step acts as a quality assurance layer, helping teams identify potential problems early. It improves code stability, reduces rework, and increases confidence when rolling out updates — a valuable advantage for enterprise-scale systems and offshore collaboration projects.
Error Handling
Error handling determines how programming languages detect and respond to mistakes — a critical factor that directly impacts system reliability, performance, and user experience when comparing TypeScript vs JavaScript performance.
- JavaScript handles errors at runtime, meaning problems are only discovered when the code is executed. While this allows quick development and testing, it can also result in bugs appearing in production, causing downtime or user-facing issues.
- TypeScript, in contrast, detects errors during development through its static typing and compilation process. Developers receive warnings and suggestions directly in their IDEs, allowing them to fix issues long before the software goes live.
For companies managing complex digital platforms or multiple development teams, this proactive error handling reduces post-release defects, debugging costs, and potential service disruptions — ultimately improving both software quality and customer satisfaction.
Tooling
Tooling refers to the development of environments, extensions, and automation tools that help engineers write, test, and maintain code efficiently.

- JavaScript benefits from a mature ecosystem built over decades, with countless libraries and frameworks such as React, Vue, and Node.js. However, its tools mainly focus on functionality rather than error prevention or code consistency.
- TypeScript, on the other hand, offers strong integration with modern IDEs like Visual Studio Code, enabling features such as real-time error detection, auto-completion, refactoring support, and intelligent code suggestions. These capabilities help teams work faster and reduce mistakes.
For businesses, better tooling translates into higher developer productivity and cleaner, more maintainable codebases. This is especially valuable for distributed or offshore teams, where consistency and clear communication between developers are essential for long-term success.
Syntax and Features
The syntax and features of a programming language shape how easily teams can write, understand, and maintain code.
- JavaScript offers a flexible and lightweight syntax, making it ideal for quick development and smaller projects. However, this flexibility can lead to inconsistent coding styles and potential errors when multiple developers contribute to the same codebase.
- TypeScript introduces structured syntax and advanced features such as interfaces, enums, generics, and type annotations. These tools make code more organized, self-documenting, and scalable, especially for enterprise-grade applications.
For business leaders, this means fewer misunderstandings between developers, faster onboarding of new team members, and smoother collaboration with offshore partners. When comparing TypeScript vs JavaScript usage, TypeScript’s structured features help companies build software that grows with the business, not against it.
Learning Curve
The learning curve determines how quickly development teams can adapt and become productive with technology.
- JavaScript has a gentle learning curve, making it one of the easiest languages for new developers to start with. Its simplicity allows teams to build prototypes or MVPs quickly, which is why it remains popular among startups and small businesses.
- TypeScript requires a bit more training due to its static typing and structured rules. However, once developers adapt, they benefit from fewer bugs, clearer code, and faster debugging.
For companies, this means that while TypeScript may take slightly longer to master initially, it delivers higher long-term productivity and better project scalability. Many enterprises find that the short investment in upskilling pays off through reduced maintenance costs and stronger development efficiency.
Pros and Cons of TypeScript and JavaScript
Both JavaScript and TypeScript offer unique advantages depending on your business goals and project scale. While JavaScript provides flexibility and speed, TypeScript emphasizes reliability and long-term maintainability.
The table below summarizes the key benefits of TypeScript vs JavaScript, as well as their drawbacks, and use cases from a business perspective.
| Criteria | JavaScript (JS) | TypeScript (TS) |
|---|---|---|
| Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
| Best Use Case | Rapid prototyping, marketing websites, or short-term projects | Long-term enterprise applications, SaaS platforms, and offshore collaboration projects |
| Business Impact | Quick launch and low initial cost but higher long-term maintenance | Higher upfront investment but stronger ROI, reliability, and scalability |
Performance, Productivity & ROI
When comparing TypeScript vs JavaScript in 2025, the real difference isn’t in raw performance — it’s in development efficiency, error prevention, and long-term return on investment (ROI).
- Performance: TypeScript and JavaScript run at the same speed because TypeScript compiles into JavaScript before execution. However, TypeScript improves code performance indirectly by reducing runtime errors and preventing inefficient code from reaching production.
- Productivity: TypeScript’s static typing and strong IDE support enable developers to identify issues early, benefit from auto-completion, and write cleaner, more maintainable code. This leads to shorter debugging cycles and smoother collaboration, especially across distributed or offshore teams.
- ROI: Although TypeScript may require a slightly higher initial investment in training and setup, companies often experience up to 25–30% fewer post-release issues and 20% faster onboarding for new developers. Over time, this translates to lower maintenance costs, better scalability, and stronger software reliability — key advantages for Singapore enterprises building long-term digital solutions.
In terms of TypeScript vs JavaScript differences, while JavaScript offers faster starts, TypeScript delivers better long-term ROI through efficiency, stability, and predictable performance across growing teams and complex systems.
When to Use TypeScript vs JavaScript
Choosing between TypeScript and JavaScript depends on your project scale, budget, and long-term goals. Both languages have their place — JavaScript excels in speed and simplicity, while TypeScript provides structure and scalability for complex, enterprise-level systems.
Use TypeScript When
Then, should I use JavaScript or TypeScript? Well, you should consider using TypeScript if your organization is focused on scalability, long-term maintenance, or multi-team collaboration. It’s particularly effective when:
- You’re building large-scale enterprise applications or SaaS platforms that will evolve over several years.
- Multiple developers or offshore teams are working together and need consistent, reliable code.
- Your project requires strict quality control, strong error prevention, and maintainable architecture.
- You want to reduce long-term technical debt and lower the cost of debugging and maintenance.
- You aim to future-proof your system with modern frameworks like Angular, React, or Next.js that natively support TypeScript.
In short, TypeScript is the smarter choice when your goal is to build durable, stable, and business-critical software with predictable ROI.
Use JavaScript When
JavaScript remains a strong choice for projects where speed, flexibility, and simplicity are the top priorities. It’s especially suitable when:
- You’re developing prototypes, landing pages, or small web applications that need to go live quickly.
- Your business has limited resources or tight timelines, and rapid deployment outweighs long-term scalability.
- You’re building applications that rely heavily on frontend interactivity but don’t require complex backend logic.
- Your team already has strong JavaScript experience and doesn’t need the additional structure of TypeScript.
- You need maximum compatibility with existing libraries, plugins, or legacy systems.
In essence, JavaScript is ideal for fast-moving projects and early-stage startups, where agility and time-to-market are more important than the long-term control and rigor that TypeScript provides.
Offshore Advantages: Web Development Projects in Singapore
For many Singapore businesses, partnering with an offshore software development company has become a strategic way to achieve cost efficiency, scalability, and faster innovation. When combined with modern technologies like TypeScript and JavaScript, offshore collaboration offers even greater value.
Singapore-based enterprises often face:
- High local developer costs and fierce competition for tech talent
- Tight project timelines driven by digital transformation goals
- Limited in-house expertise in specialized technologies
Partnering with offshore web development vendors — particularly in nearby markets like Vietnam — helps address these challenges by providing:
- Access to skilled engineers experienced in global frameworks such as React, Angular, and Node.js
- Significant cost savings, often 30–50% lower than local development rates
- Flexible engagement models (project-based, dedicated team, or staff augmentation)
- Round-the-clock productivity, with distributed teams covering different time zones
- Enhanced code quality and collaboration when using TypeScript for structured, scalable development
By combining offshore talent with the right technology stack, Singapore companies can scale faster, reduce risk, and maintain development quality, while focusing internal resources on strategic growth.
Kaopiz: Your Trusted Partner for TypeScript vs JavaScript Development in Singapore
With over a decade of experience and a team of 600+ skilled engineers, Kaopiz helps Singapore enterprises build reliable, high-performance software using TypeScript and JavaScript. We offer excellent offshore software development services, combining technical expertise, cost efficiency, and deep industry understanding to turn your digital vision into reality.

Here’s why businesses choose Kaopiz:
- Proven Expertise: Over 10 years of experience delivering 1,000+ successful projects across industries such as finance, retail, manufacturing, and education.
- Skilled Development Team: A team of 600+ engineers, including senior TypeScript and JavaScript specialists, supported by bilingual BrSEs for seamless communication.
- Strong Credentials: Recognized as an AWS Advanced Consulting Partner, ISO 27001 certified, and an ISTQB Platinum Partner, ensuring both quality and security.
- Flexible Engagement Models: From dedicated teams to full project outsourcing, Kaopiz offers scalable solutions tailored to your business needs and timelines.
- Cost Efficiency with Quality Assurance: Based in Vietnam, Kaopiz delivers high technical quality at competitive rates, helping Singapore companies optimize budgets without compromising results.
Kaopiz’s blend of technical excellence, project transparency, and cross-border collaboration experience makes it the ideal partner for businesses aiming to scale efficiently with TypeScript or JavaScript in 2025 and beyond.
Future Outlook in Singapore (2025–2030): TypeScript as the New Enterprise Standard
As enterprise systems grow in complexity and digital transformation accelerates across Singapore, many organizations are transitioning from pure JavaScript stacks to TypeScript-based architectures. This shift reflects a global trend: TypeScript is increasingly seen not just as a developer tool, but as a strategic asset for reducing technical debt, improving system reliability, and supporting distributed teams.
Between 2025 and 2030, we expect TypeScript usage to become the default choice for large-scale web applications, especially among institutions, fintechs, and tech-forward SMEs in Singapore.
Below are three crucial perspectives to understand this transition:
Why Are Singapore Companies Moving Toward TypeScript in 2025?
- The demand for higher-quality, maintainable software in sectors like finance, government, and fintech is pushing companies to adopt more robust tooling.
- According to industry surveys, TypeScript adoption surged from ~12% in 2017 to ~35% in 2024, signaling strong momentum in developer preference.
- In Singapore’s context, digitalization policies and Smart Nation initiatives are encouraging enterprises to adopt scalable, long-lasting solutions rather than short-term patches.
How Does TypeScript Improve Performance, Productivity, and ROI?
- Though runtime performance is similar (since TypeScript transpiles to JavaScript), the gains come in productivity — fewer bugs, better tooling, and faster debugging cycles.
- Improvements in compile-time checks and IDE integration reduce developer waste and enable teams to deliver features more reliably.
- Over time, the lower maintenance cost, fewer production issues, and better code longevity yield stronger ROI, making TypeScript economically advantageous for long-term projects.
How Can Kaopiz Help with TypeScript Development in Singapore?
- Kaopiz offers dedicated TypeScript migration services and new-build solutions tailored for Singapore firms, supported by our bilingual bridging engineers to facilitate smooth cross-border collaboration.
- With deep experience in both JavaScript and TypeScript stacks, we can provide architectural consulting, code audits, incremental refactoring, and full development services.
- We partner on projects of every scale — from MVPs to enterprise systems — ensuring quality, maintainability, and alignment with Singapore’s regulatory and performance standards.
With a proven track record in JavaScript and TypeScript development, Kaopiz helps companies across Singapore design, build, and scale their digital solutions with confidence. Whether you’re modernizing legacy systems or developing a new platform from scratch, our team delivers reliable offshore development backed by quality, transparency, and cost efficiency.
Ready to modernize your tech stack?
Partner with Kaopiz — your trusted web development company in Singapore — to turn your next project into a lasting success.
Conclusion
Is TypeScript better than JavaScript? Both TypeScript vs JavaScript play essential roles in modern web development. JavaScript remains ideal for fast-moving, lightweight projects, while TypeScript has emerged as the enterprise standard for scalable, secure, and high-quality software.
For Singapore businesses accelerating digital transformation under Smart Nation and Industry 4.0 initiatives, adopting TypeScript isn’t just a technical upgrade — it’s a strategic decision that improves team efficiency, reduces long-term costs, and strengthens ROI.
FAQs
- Why Are More Singapore Companies Switching from JavaScript to TypeScript in 2025?
- Because TypeScript offers better scalability, stability, and maintainability. As projects grow more complex, TypeScript’s static typing helps teams detect errors early and deliver cleaner, more reliable software — key for enterprises modernizing under Singapore’s Smart Nation initiatives.
- Does TypeScript Help Reduce Development Costs When Outsourcing Offshore Vendors?
- Yes. TypeScript’s built-in type checking and clearer code structure reduce miscommunication and rework, which are common in distributed teams. Offshore vendors can deliver higher-quality output faster, resulting in lower overall development and maintenance costs.
- How Hard Is It to Migrate from JavaScript to TypeScript?
- Migration is typically incremental and manageable. Teams can convert existing JavaScript files step by step while maintaining functionality. With the right guidance from experienced developers or IT outsourcing companies in Singapore like Kaopiz, the transition can be smooth and low-risk.
- How Can Offshore Teams in Vietnam or Other Countries Collaborate Effectively Using TypeScript?
- TypeScript’s strict structure and self-documenting code make it easier for offshore teams to collaborate consistently. It improves code readability, reduces misunderstandings, and allows faster onboarding for new developers — ensuring productivity across time zones.
- Should Singapore startups or SMEs use JavaScript or TypeScript for new projects?
- For quick prototypes or short-term projects, JavaScript may be sufficient. However, for startups and SMEs aiming to scale or attract investment, TypeScript provides a stronger foundation with fewer bugs, better maintainability, and higher long-term ROI.
Trending Post



















No Comments yet!